2.3 Understanding Installation Scenarios
While you can configure MailMarshal to run in many environments, there are two basic configurations to consider, based on the number of users and your typical email volume:
•Standalone, or basic installation (several variations available)
•Array installation
The standalone installation scenario is appropriate for small to mid-size organizations with a lower volume of email. This option allows smaller organizations to gain all the benefits of using MailMarshal to reduce email volume and block annoying and costly spam.
The array installation is appropriate for larger, distributed organizations where email volume is high, or where use of a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is necessary. This option provides all the security and efficiency options larger organizations require.
For more information about determining your configuration needs, see the Technical Reference titled “MailMarshal Sizing Guide” at www.trustwave.com, or contact your Technical Support representative.
For small to medium-sized organizations, a standalone installation provides convenience and value. In a standalone installation, you install all the MailMarshal components as well as the SQL Express or Microsoft SQL Server database on a single computer.
To use the MailMarshal Spam Quarantine Management Website or Marshal Reporting Console, install these components on a Microsoft IIS Server.
You can configure a standalone installation of MailMarshal in the following ways:
•As a POP3/SMTP server (for very small organizations)
•As an internal email relay to your email server
•On your existing email server
Each option provides all the required functions of an email gateway. Other variations are also possible.
2.3.1.1 MailMarshal as Email Server
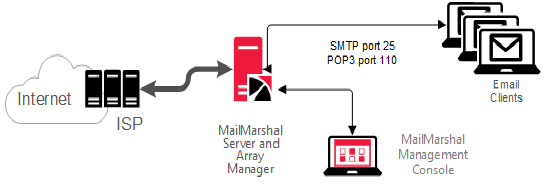
You can install MailMarshal to function as a POP3/SMTP email server, providing all email server functions for a small organization, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: MailMarshal as email server

In this scenario, MailMarshal receives and processes all incoming email. MailMarshal receives email on port 25 from within the organization and delivers email to internal POP3 mailboxes on port 110. MailMarshal receives and sends email to and from external addresses over your Internet link.
For this configuration, install the Server and Array Manager components on a single computer. Most organizations that choose this configuration can also install Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Express on the same computer to host the MailMarshal database.
2.3.1.2 MailMarshal as an Internal Email Relay
You can install MailMarshal on a separate computer to act as an email relay within an organization, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 3: MailMarshal as email relay
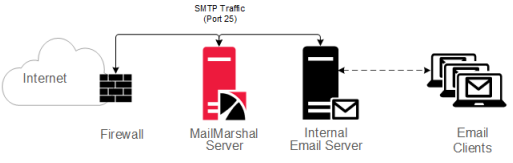
This option is suitable for small to medium-sized organizations with a single Internet gateway and email server. In this scenario, the MailMarshal Server receives inbound email on port 25, processes it, and forwards it for delivery to the existing email server. The email server forwards all outbound messages to the MailMarshal Server for processing and delivery.
For this configuration, install the MailMarshal Server and Array Manager components on a separate computer from the existing email server. Set the Domain Name Service Mail Exchange (DNS MX) records or firewall relay settings so the MailMarshal Server receives all inbound email.
Most organizations that choose this configuration can also install Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Express on the same computer to host the MailMarshal database.
2.3.1.3 MailMarshal on Existing Email Server
You can install MailMarshal on your existing email server computer, as shown in the following figure.
Figure 4: MailMarshal installed on internal email server
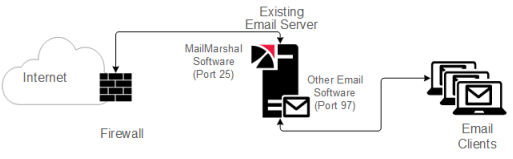
MailMarshal receives all inbound email on default SMTP port 25, processes the email, and forwards email to the existing email server using the localhost IP address on port 97 for delivery. The existing email server forwards outbound email to MailMarshal on port 25 using the localhost IP address.
In this case, your email server must have sufficient resources to support both MailMarshal and another email server application. Install the MailMarshal Server and Array Manager components on your existing email server. Many organizations that choose this configuration can also install Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Express on the same computer to host the MailMarshal database.
When you install MailMarshal on the same physical server as the existing email server software, normally you do not need to change the inbound routing. However, because MailMarshal takes on the role of listening for SMTP traffic on port 25, you must configure your existing email server to listen for SMTP traffic on another port. Many organizations use port 97 for this purpose, but you can configure your existing email server to listen on any free TCP port.
This configuration is not suitable if you have multiple internal email servers (SMTP or Exchange). With multiple internal email servers, install MailMarshal on a separate computer as an email relay. For more information, see “MailMarshal as an Internal Email Relay”.
You can install an array of MailMarshal Servers in a variety of configurations to manage email for larger enterprises. MailMarshal provides a broad range of enterprise configurations that can include redundancy and failover support. The following figure shows a typical MailMarshal array configuration.
Figure 5: MailMarshal Array installation
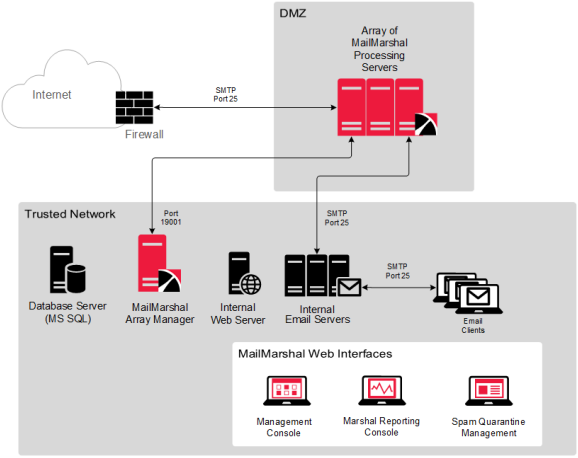
In this scenario, you can install the MailMarshal Server component on a number of computers to create an array of MailMarshal email processing servers in a Demilitarized Zone (DMZ). The DMZ is a part of a local network that has controlled access both to the Internet and to the internal network of the organization.
To provide load balancing, you can install the email processing servers in a cluster using third-party software, such as a Datacenter Server.
A distributed enterprise with more than one email gateway can install one or more MailMarshal Servers at each gateway. If you use the same email policy at all locations, you can control the MailMarshal configuration and perform logging for all gateways using a single MailMarshal Array Manager. All MailMarshal Servers must be able to communicate with the Array Manager computer over port 19001.
The MailMarshal Servers receive all incoming email on port 25. MailMarshal Servers transfer email to and from local email servers on port 25. The MailMarshal Array Manager requires a single port opening to the DMZ to configure the MailMarshal Servers and receive log data (port 19001 by default).
Install the MailMarshal Array Manager, and the database if possible, on a dedicated computer inside the trusted network. The location of the Array Manager can affect the performance of the administration and configuration tools used in MailMarshal, but does not affect email processing performance.
For best results, install the MailMarshal Array Manager component in one of the following locations, listed from most-preferred to least-preferred:
•On the same server as the Microsoft SQL Server hosting the database. Since the Array Manager is the only MailMarshal component that communicates directly with the database, installing the Array Manager on the computer that hosts Microsoft SQL Server or SQL Express results in the most efficient operation.
•On another computer in the network close to the computer hosting the database over a high-speed network connection.
•On an Active Directory Global Catalog or other Directory Server. The Array Manager communicates regularly to the Global Catalog if you are running Active directory, or through LDAP to another existing Directory Server.
•The MailMarshal Management Console website is installed on the Array Manager server and can be accessed by web browser clients.
•To use the MailMarshal Spam Quarantine Management Website or Marshal Reporting Console, install these components on a Microsoft IIS Server domain member inside the network.