This article applies to:
- Trustwave MailMarshal (SEG)
Question:
- What are the advanced options for configuring Routes, Local Domains, and Anti-Relaying?
- How do MailMarshal Routing Tables, Local Domain Tables, and anti-Relaying Tables work?
Information:
Current versions of MailMarshal have a flexible framework for Routing, Anti-Relaying, and Local Domains setup. This article explains how these three items are related and gives some examples of advanced configurations.
Local Domains
Local Domains define the email addresses that MailMarshal SMTP accepts for inbound local delivery.
In current versions of MailMarshal SMTP, email for local domains can be delivered by any valid routing method as defined in a Routing Table. In earlier versions, local domain email was delivered to specific IP addresses.
Routing Tables
Routing tables determine how and where MailMarshal SMTP delivers email messages.
In current versions you can configure any number of delivery routes for any domains, including local domains, default (outbound) delivery, and any number of specific domains. You can set routing to an IP address, hostname, DNS, or MailMarshal POP3. The Routing Tables can also include multiple load balanced and/or fallback entries. You can set up a different Routing Table for each processing server in a MailMarshal Array.
Relaying Tables
Relaying tables define the sources that are permitted to send outbound email through MailMarshal SMTP. "Outbound email" is email not addressed to Local Domain addresses.
In current versions of MailMarshal SMTP, you can configure relaying permissions by IP address, IP range, hostname, or MX lookup of DNS records for a domain. You can set up a different Relaying Table for each processing server in a MailMarshal Array.
Note: Your Relaying Table should NEVER allow relaying from your firewall or service provider IP address. Relaying Tables control email addressed to external recipients. MailMarshal ALWAYS accepts email addressed to internal recipients (in your local domains).
Default Setup
The MailMarshal SMTP Configuration Wizard creates a minimum setup for email delivery. This setup uses a single IP address for all local domain delivery. Relaying is allowed from the same IP address. All outbound email is delivered using DNS lookup.
The default setup suits the typical case of a small to medium sized organization that has a single MailMarshal server and a single internal email server (such as Microsoft Exchange).

| Routing Table |
| Destination |
Route |
Priority |
| Local Domains |
192.168.3.5:25 |
|
| * |
DNS |
|
| Relaying Table |
| Source |
Type |
Allowed |
| 192.168.3.5 |
IP |
Allowed |
Multiple Local Domains
An organization may have multiple local domains, and some local domains may have their own internal email servers.
- You can create a Routing Table that directs email for a specific domain to a different location.
- Ensure that the spedific domain entry is above the Local Domains entry so it will be evaluated first.
- The Relaying Table should normally include the same servers as the Routing Table, to allow outbound email from each local server.
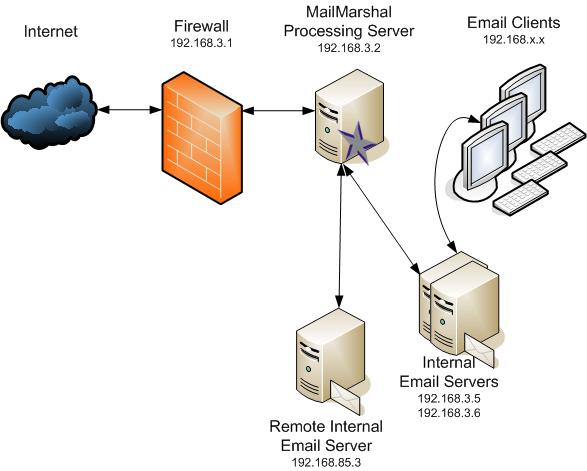
| Routing Table |
| Destination |
Route |
Priority |
| remote.example.com |
192.168.85.3:25 |
|
| Local Domains |
192.168.3.5:25
192.168.3.6:25
|
10
10 |
| Relaying Table |
| Source |
Type |
Allowed |
| 192.168.85.3 |
IP |
Allowed |
| 192.168.3.5 |
IP |
Allowed |
| 192.168.3.6 |
IP |
Allowed |
Load-Balanced Internal Connections
An organization with multiple internal email servers may want to load-balance internal delivery.
- You can create a Routing Table with multiple Local Domains entries with the same priority.
- The Relaying Table should normally include the same servers as the Routing Table, to allow outbound email from each clustered server.
- Refer to the example tables above.
Multiple External Routes
An organization may have multiple external connections.
- If all outbound email is delivered through an ISP, the most efficient method may be to configure a default route using the server name for the ISP's email server. This method will automatically configure fallback or load-balanced routing depending on the MX record priorities set by the ISP.
- If outbound email can be delivered through more than one ISP, you can configure load-balanced or fallback routes using all of the available servers.
| Routing Table |
| Destination |
Route |
Priority |
| Local Domains |
192.168.85.3:25 |
|
| * |
smtp.bigISP.com:25
mail1.OtherISP.com:25
mail2.OtherISP.com:25
|
10
20
20 |
| Relaying Table |
| Source |
Type |
Allowed |
| 192.168.85.3 |
IP |
Allowed |
MailMarshal POP3 Setup
An organization using MailMarshal POP3 server typically requires additional Relay Table setup.
- Include the entire local network in the Relay Table, so all workstations can send outbound email directly through the MailMarshal server.
- However, be sure to deny your firewall or other external connection, so that you do not offer an open relay.
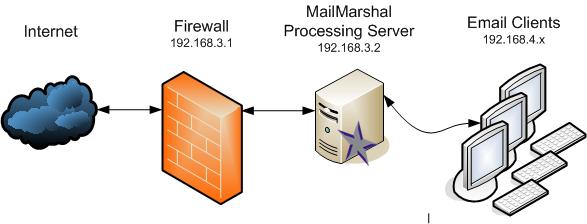
| Routing Table |
| Destination |
Route |
Priority |
| Local Domains |
POP3 |
|
| * |
DNS |
|
| Relaying Table |
| Source |
Type |
Allowed |
| 192.168.3.1 |
IP |
Denied |
| 192.168.4.1-192.168.4.255 |
IP Range |
Allowed |